
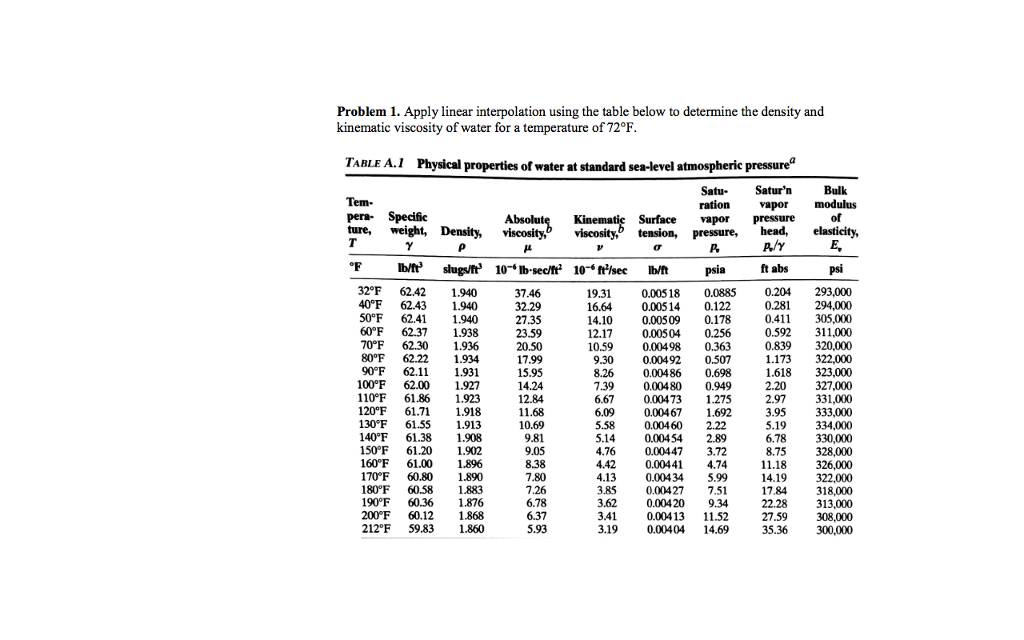
τ = Shear stress acting on the fluid layer in contact with the moving plate.The viscosity of a Newtonian fluid is linearly proportional to the shear stress in a one-dimensional flow. The Reynolds number, which connects the fluid’s momentum to its viscous forces, is one formulation that makes use of kinematic viscosity. The kinematic viscosity ν=μ/ρ seems often in fluid mechanics and warmth switch and is associated with flows below the pressure of gravity. When managing surprise waves and phenomena that consist of excessive and fast compression of the fluid, the majority viscosity η can’t be neglected, being associated with essential principles together with sound attenuation. Viscosity example boundary layer Kinematic Viscosity
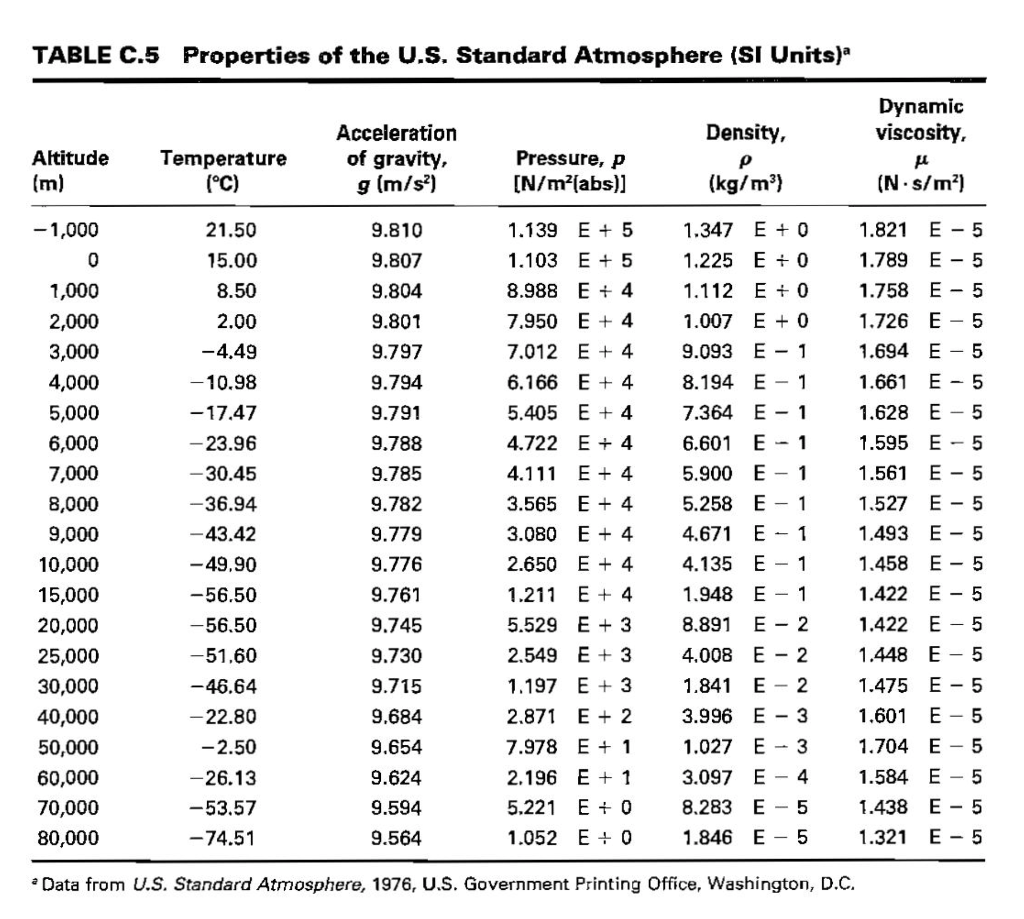
In totality, we can say there are three types of viscosity, However, relying on waft physics distinctive viscosities play corresponding essential roles. The maximum usually used withinside the area of fluid dynamics is shear or dynamic viscosity. Poisesulle’s Law is the name given to this concept today, and it is employed in a variety of formulas and equations. For example, he discovered from this experiment that a liquid’s velocity depends on viscosity, provided that the tube’s length and diameter are constant.John-Louis-Marie Poiseuille discovered viscosity in 1829 by testing the flow of liquids through a variety of thin tubes of varying sizes and shapes.John-Louis-Marie Poiseuille and Gotthilf Hagen were the three men who molded viscosity into what it is today.Each of these experts discovered principles that have been combined to aid scientists today build new experiments and calculations. The discovery of viscosity is remarkable in that it was made three times independently by three distinct scientists, which makes it particularly interesting.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
